Navigating the 11 Team Double Elimination Bracket: A Comprehensive Guide
The 11 team double elimination bracket is a tournament format frequently used in competitive settings, offering teams a second chance after an initial loss. This format ensures a fairer and more competitive environment compared to single-elimination brackets. Understanding how to seed and navigate this type of bracket is crucial for both organizers and participants. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the 11 team double elimination bracket, covering seeding strategies, bracket structure, and key considerations for running a successful tournament.
Understanding Double Elimination Brackets
Before diving into the specifics of an 11 team double elimination bracket, it’s essential to understand the general principles of double elimination tournaments. In a double elimination format, each team must lose two matches to be eliminated from the tournament. This contrasts with single elimination, where a single loss results in elimination. This structure provides a more robust measure of a team’s overall performance, reducing the impact of a single bad game or unfavorable matchup.
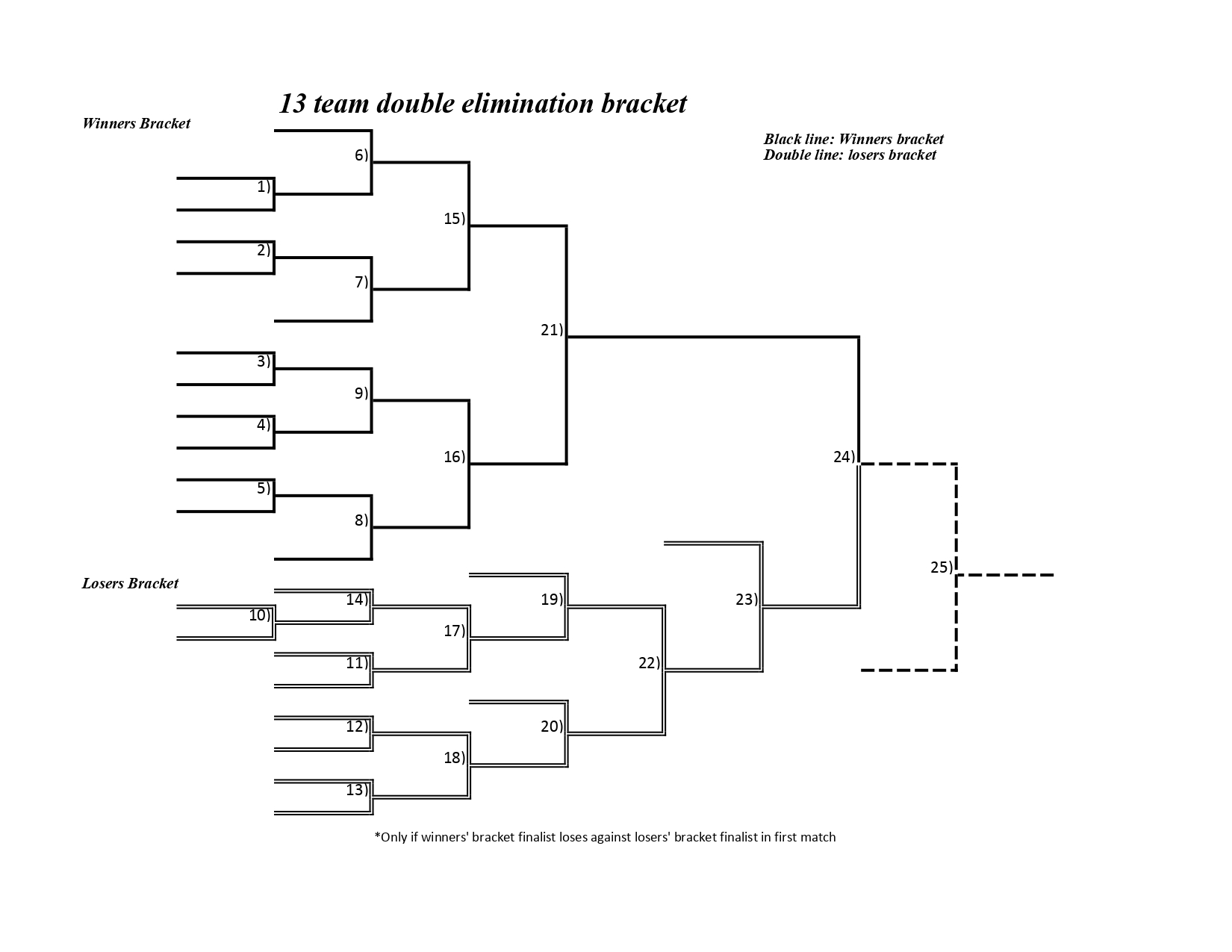
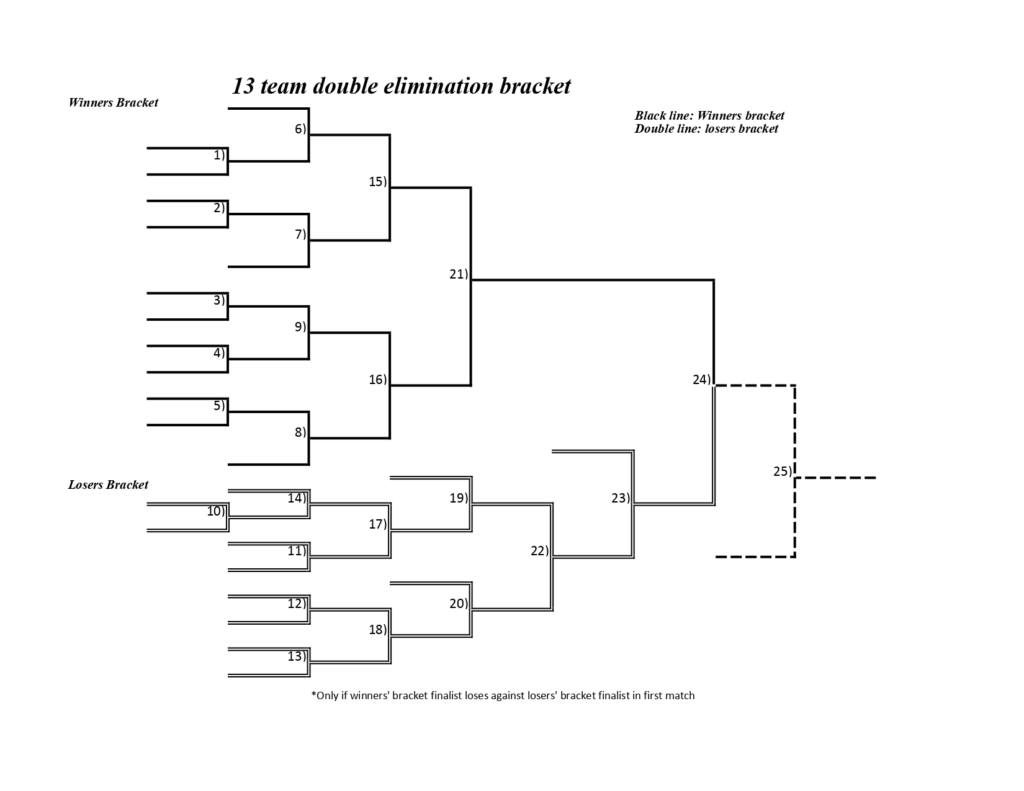
The bracket is divided into two main sections: the winners bracket and the losers bracket (sometimes called the consolation bracket). Teams start in the winners bracket, and those who lose a match are moved to the losers bracket. Teams in the losers bracket must win consecutive matches to stay in the tournament. Eventually, the winner of the winners bracket faces the winner of the losers bracket in the grand final. Because the team from the winners bracket has not lost a game yet, the team coming from the losers bracket must beat them twice to win the tournament, otherwise, the team from the winner’s bracket wins the tournament if they win the first game. This is often referred to as a “bracket reset”.
Seeding an 11 Team Double Elimination Bracket
Seeding is a critical aspect of any tournament, as it aims to ensure that the strongest teams are less likely to meet each other early in the competition. For an 11 team double elimination bracket, several seeding methods can be employed, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
Common Seeding Methods
- Random Seeding: This is the simplest method, where teams are randomly assigned positions in the bracket. While easy to implement, it doesn’t account for team strength and can lead to unbalanced matchups early on.
- Ranked Seeding: Teams are seeded based on their prior performance, rankings, or other objective measures of skill. This method is generally preferred, as it aims to create a more balanced and competitive tournament.
- Geographical Seeding: Teams are seeded based on their geographical location. This is often used in tournaments with regional representation to avoid early matchups between teams from the same area.
- Committee Seeding: A selection committee uses a combination of objective data and subjective evaluation to determine the seeding. This method allows for more nuanced consideration of team strength but can be prone to bias.
Specific Seeding Considerations for 11 Teams
When seeding an 11 team double elimination bracket, the goal is to distribute the top teams as evenly as possible throughout the bracket. With 11 teams, some teams will receive byes in the first round, meaning they automatically advance to the second round. It’s generally best practice to award these byes to the highest-seeded teams.
Here’s a common approach for seeding an 11 team double elimination bracket:
- Rank the teams from 1 to 11 based on their seeding criteria.
- Assign byes to the top 5 seeded teams (teams ranked 1-5).
- Place the remaining 6 teams (teams ranked 6-11) in the first-round matches.
The specific placement of teams within the bracket can vary, but a common arrangement is to have the highest-seeded teams with byes positioned such that they don’t meet each other until later rounds. This helps ensure that the strongest teams have a higher chance of advancing deep into the tournament.
Structuring the 11 Team Double Elimination Bracket
The structure of an 11 team double elimination bracket is designed to accommodate the double elimination format while efficiently progressing through the tournament. The bracket typically consists of two main sections: the winners bracket and the losers bracket.
Winners Bracket
The winners bracket starts with all 11 teams. The top 5 seeded teams receive byes into the second round. The remaining 6 teams play in the first round, with the 3 winners advancing to the second round to join the teams with byes. From the second round onwards, all matches are played until a single team remains undefeated as the winner of the winners bracket.
Losers Bracket
The losers bracket is where teams go after losing a match in the winners bracket. The bracket is structured to allow these teams to compete for a chance to reach the grand final. Teams dropping from the winners bracket are placed into the losers bracket at different stages, depending on when they lost in the winners bracket. The losers bracket requires teams to win consecutive matches to stay in contention.
Grand Final
The grand final is the culminating match of the tournament, where the winner of the winners bracket faces the winner of the losers bracket. As mentioned earlier, the team from the winners bracket has the advantage of not having lost a match yet. Therefore, the team coming from the losers bracket must defeat the winners bracket team twice to win the tournament. If the winners bracket team wins the first match, they are crowned the champions.
Key Considerations for Running an 11 Team Double Elimination Tournament
Successfully running an 11 team double elimination bracket tournament requires careful planning and execution. Here are some key considerations:
- Scheduling: Create a realistic schedule that allows enough time for all matches, including potential bracket resets in the grand final. Consider the availability of venues, referees, and players.
- Communication: Clearly communicate the tournament rules, schedule, and bracket structure to all participants. Use a reliable communication channel to keep teams updated on any changes or announcements.
- Fair Play: Enforce the tournament rules fairly and consistently. Address any disputes or issues promptly and impartially.
- Bracket Management: Use a reliable bracket management system to track match results, update the bracket, and display the standings. This can be done manually or using online tournament platforms.
- Venue and Equipment: Ensure that the venue is suitable for the tournament and that all necessary equipment is available and in good working order.
Advantages of Using a Double Elimination Bracket
The 11 team double elimination bracket, like other double elimination formats, offers several advantages over single elimination:
- Fairness: Provides a second chance for teams that may have had a bad game or an unlucky matchup early on.
- Accuracy: More accurately reflects the overall strength of the teams, as it requires teams to lose twice to be eliminated.
- Excitement: Creates more competitive and exciting matches, as teams in the losers bracket fight to stay in the tournament.
- Increased Participation: Encourages more teams to participate, as they know they have a second chance to compete.
Disadvantages of Using a Double Elimination Bracket
Despite its advantages, the 11 team double elimination bracket also has some drawbacks:
- Time: Requires more matches and therefore more time to complete than a single elimination bracket.
- Complexity: Can be more complex to understand and manage than a single elimination bracket.
- Resources: May require more resources, such as venues, referees, and staff, to run successfully.
Tools for Managing 11 Team Double Elimination Brackets
Several tools and platforms are available to help manage 11 team double elimination brackets. These tools can automate tasks such as bracket generation, scheduling, result tracking, and standings display. Some popular options include:
- Challonge: A widely used online tournament platform that supports various bracket formats, including double elimination.
- Toornament: Another popular platform with robust features for managing tournaments and leagues.
- BracketMaker: A simple and free tool for creating and customizing brackets.
- Google Sheets/Excel: For smaller tournaments, a spreadsheet can be used to manually create and manage the bracket.
Conclusion
The 11 team double elimination bracket is a valuable tournament format for creating a fair and competitive environment. By understanding the principles of double elimination, employing effective seeding strategies, and utilizing appropriate management tools, organizers can run successful and engaging tournaments. While it may require more time and resources than single elimination, the benefits of increased fairness and accuracy make it a worthwhile choice for many competitive settings. When properly implemented, an 11 team double elimination bracket offers a compelling and rewarding experience for both participants and spectators alike. The key is to plan well, communicate effectively, and ensure fair play throughout the tournament. Remember to consider the strengths and weaknesses of each team when seeding and to use the tools available to ensure a smooth and efficient tournament. [See also: Single Elimination vs. Double Elimination Brackets] [See also: Tournament Seeding Strategies] [See also: Best Tournament Management Software]